When you’ve been browsing a website, seen and bought a few things you like, and when they email you it’s like someone has been reading your mind. All the products included are exactly what you’re into, tailored to your interests and budget.
Welcome to the world of AI-powered hyper-personalisation, the distinctions between the top 30 providers are significant. This is where shopping online is like having a personal concierge who knows your needs and preferences inside out. This isn’t a glimpse into a distant future; its hyper-personalisation and appreciation of how powerful it is, are the fastest adoption criteria for marketers at this precise moment.
tl;dr (too long: didn’t read)
- DEFINITION. Hyper-personalisation uses real-time data and AI to create customised experiences for an individual customer.
- PERSONALISATION VS. HYPER-PERSONALISATION. Personalisation offers general recommendations based on past behaviour, while hyper-personalisation provides real-time, context-aware experiences.
- EXAMPLES. Examples of hyper-personalisation include personalised product offerings based on individual spending habits, style, price, could, material, brand or fit.
- BENEFITS. Hyper-personalisation enhances customer engagement, removes sales obstacles, boosts conversions, and delivers immediate customer empathy.
- HOW IT WORKS. Hyper-personalisation involves collecting data, analysing it, building customer profiles, forecasting future behaviour, and providing real-time and personalized communication.
- TECHNOLOGIES. Hyper-personalisation leverages technologies like AI, ML, LLMs and Data Analytics, Big Data, predictive analytics, NLP, CRM, IoT, and quantum computing.
- CASE STUDIES. Hyper-personalisation is being used across ecommerce, with all the big research companies confirming its prowess.
- CHALLENGES. Implementing hyper-personalisation requires careful consideration of privacy, data collection, legal compliance, and algorithm bias to ensure customer trust and fairness.
Hyper-personalisation explained?
Hyper-personalisation is the process of using real-time data and advanced technologies like AI and machine learning to provide highly relevant and personalised experiences to each user.
Personalisation vs. hyper-personalisation
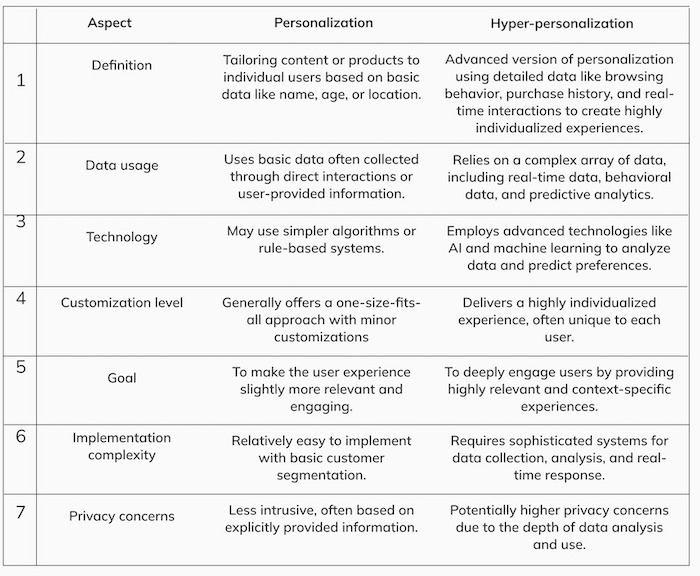
What is personalisation vs. hyper-personalisation?
Personalisation involves tailoring experiences based on basic user information including segmentation, while hyper-personalisation strategies use advanced data analysis, including real-time data, to create highly specific and individualised user experiences.
Hyper personalisation is the next level of tailored customer experiences. Unlike basic personalisation, which might just use your name in an email, hyper-personalisation digs infinitely deeper. It uses data like browsing history, purchase patterns, and preferences to offer a truly individualised experience.
Why is hyper-personalisation so good?
The Deloitte report found that 80% of customers are more likely to purchase from a company that offers personalised experiences. Moreover, 69% of online shoppers say that the quality or relevance of a company’s message influences their perception of the brand. These findings suggest that hyper-personalisation is a powerful tool that can help businesses improve their customer satisfaction, loyalty, and sales.
- Enhanced customer engagement and satisfaction: Customers love feeling understood. Hyper-personalisation makes them feel special and valued, leading to a stronger connection with the brand.
- Removing obstacles from the sales process that could complicate user experience. Hyper-personalisation avoids overwhelming customers with too many choices and smartly highlights products that resonate with their specific needs and preferences. This way, you can address customer pain points and provide optimal solutions. (This doesn’t mean stocking fewer products, but rather employing a solution to identify from all the ones you have, which products are most pertinent to that individual).
- Increased conversion rates and sales growth: When customers see products that resonate with their needs, they’re more likely to buy.
- Customer loyalty and advocacy: Hyper-personalised experiences foster deeper customer connections, leading to increased brand loyalty, advocacy, and customer lifetime value.
How does hyper-personalisation work?
To explain how hyper-personalisation works, let’s use the example of an online retail store and break it down into steps:
- Data collection: The first step involves gathering data. For our online retail store, this includes tracking user behaviour data such as browsing history, purchase history, items added to the cart but not purchased, search queries, and even time spent on specific product pages.
- Data analysis using AI and ML: The collected data is then analysed using AI and machine learning algorithms. These technologies identify patterns in the data – for instance, if a user frequently views sports apparel or if they tend to purchase items during seasonal sales.
- Building customer profiles: Based on the analysis, a detailed customer profile is created. This profile includes not just the basic demographics of the user but also their preferences, buying habits, and potential interests.
- Predictive analytics: The system then uses predictive analytics to forecast future behaviour. For example, if a user regularly buys running shoes every six months, the system predicts when they are likely to make their next purchase.
- Real-time personalisation: As the user interacts with the site, real-time personalisation kicks in. If the user is browsing running shoes, the system might immediately display the latest models, deals on their preferred brands, or complementary products like athletic socks or fitness trackers.
- Customized communication: Hyper-personalization also extends to communication. The retail store sends out personalized emails or app notifications, perhaps alerting users about an upcoming sale on sports gear or new arrivals in their preferred brand.
- Feedback loop: Finally, the user’s response to these personalised experiences is fed back into the system, continuously refining the personalisation algorithms. For example, if the user purchases a recommended product or clicks on a personalised email link, that information is used to further tailor future recommendations and communications.
- Autonomous Communication: By far the greatest return from hyper-personalisation comes through email marketing. Consumers spend far more time offline than they do on it. Therefore, they are 99% more likely to make a purchase when they are not on your site. Sending them details of their selection to them at that precise time is the essence of AI technology. And by autonomous we mean with zero human involvement whatsoever.
Throughout this process, the key is the seamless integration of various technologies and the continual learning and adaptation of the system based on user interactions. This creates a highly personalised shopping experience, where each user feels the retail site is uniquely attuned to their preferences and needs.
Hyper-personalisation, thus, not only enhances the user experience but also significantly increases the likelihood of user engagement and sales conversion.
The role of technology in hyper-personalisation
The key technologies driving hyper-personalisation include:
- Artificial intelligence: Employs algorithms to analyze user data and make predictions or decisions.
- Machine learning: A subset of AI that enables systems to learn and improve from experience without being explicitly programmed.
- Data analytics: Involves examining large data sets to uncover hidden patterns, correlations, and insights.
- Big Data technologies: Facilitate the handling of enormous volumes of data that feed into personalisation algorithms.
- Predictive analytics: Uses statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to identify the likelihood of future outcomes based on historical data.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Enables computers to understand, interpret, and respond to human language in a useful way.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems: Help in collecting and managing customer data, which is essential for personalisation.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Connects everyday devices to the internet, providing more data points for personalisation.
- Cloud computing: Offers the necessary infrastructure and scalability for storing and processing large data sets used in hyper-personalisation.
Example of hyper-personalisation in ecommerce
Hyper-personalisation solutions create unique emails for each consumer using only first-party data captured on the user’s site. It uses predictive analytics and machine learning. This method analyses a user’s purchase history, browser history, frequency of viewing products, and length of time spent looking at each product and compares it with many many others to identify sequential ranking and hyper-personalised parameters for purchase selection for each individual.
Stitch Fix uses AI and ML to personalise fashion recommendations and create individualized online stores for customers. They collect extensive data on customer preferences and sizes, using a gamified feedback system to refine style selections.
Their algorithms, including a foundational “latent style” model, help curate highly tailored fashion items and outfits. Stitch Fix also maintains human stylists in the loop, who use algorithmic suggestions and customer notes to fine-tune selections.
This blend of technology and human input optimises customer satisfaction and reduces return rates, with a significant portion of sales coming from these personalised recommendations.
Challenges in implementing hyper-personalisation
- Privacy concerns: With great personalisation comes great responsibility for privacy. Customers want personalized experiences but also value their data privacy. Hyper-personalisation can lead to… hyper-personalized social engineering attacks, as it was with the above-mentioned 23andMe (hackers stole ancestry data on 6.9 million users).
- Data collection: Accurate and comprehensive data collection is key. The more data you have, the better the personalization, but it has to be collected ethically and legally.
- Legal issues: Compliance with laws are crucial. Businesses must ensure they’re using data in a way that respects customers’ rights.
- Algorithm bias: AI algorithms used for hyper-personalisation are trained on data, and if the data is biased, the algorithms will reflect that bias. This can lead to unfair or discriminatory treatment of certain groups of customers.
Conclusion
What is the future of hyper-personalisation? When it comes to reasons for marketing professionals to use artificial intelligence (AI) to improve customer experience (CX) worldwide, 40% of marketers surveyed named “personalisation, even hyper-personalisation as the number three reason to do it.
According to A2Z Market Research, the global hyper-personalisation market is expected to grow at a significant CAGR of +11% during the forecasting period by 2030.
Hyper-personalisation is reshaping how businesses interact with customers. We will see more personalised product recommendations, than any other products and services around us. Our digital experience is going to become more personal than ever before.
To know more about installing a hyper-personalisation plugin to your site today contact us, we will be delighted to help you.





