Ecommerce hyper-personalisation is the practice of delivering product offerings to individuals quid-pro-quo for using their data, demonstrating both appreciation of both their custom and loyalty to you and the courtesy of using it for their comfort and ease of shopping. We don’t aim to manipulate customers into alternate product selections or to influence their loyalties. Instead, we simply aim to perpetuate their choices, their desires and their preferences. This results in massive increases in basket size, and in turn lifetime customer value that obliterates conventional solutions.
Personalisation is increasingly important to merchants seeking to not only engage shoppers but to also increase repeat purchases, drive sales, and increase conversion. Various highly respected market research organisations have illustrated without a doubt that it is the fastest-growing aspect of ecommerce marketing. That delivers a 20-fold increase by its immediate adoption, which explains the importance.
Benefits of Hyper-personalisation in Ecommerce (With Stats!)
Before the explosion of digital commerce, customers simply walked into stores and found a friendly clerk who helped them find what they wanted.
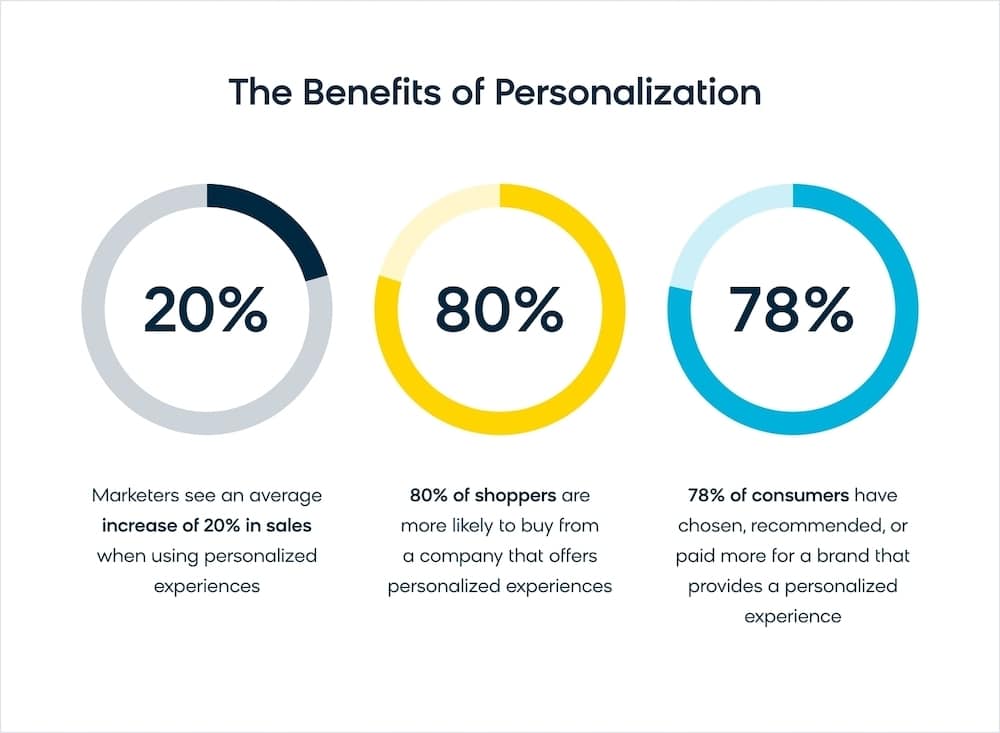
Consider these ecommerce personalisation stats:
Marketers see an average increase of 20% in sales when using hyper-personalised experiences. (Monetate)
80% of shoppers are more likely to buy from a company that offers hyper-personalised experiences. (Epsilon)
60% of consumers say that they will likely become repeat buyers after a personalised shopping experience with a particular company. (Segment)
78% of consumers have chosen, recommended, or paid more for a brand that provides a hyper-personalised service or experience. (McKinsey)
53% of digital experience delivery professionals said they lack the right technology to hyper-personalise experiences. (Forrester)
These are the game-changing facts of hyper-personalisation — it not only helps your customers achieve their goals while engaging with your brand but can also align with your business goals when the right strategy is in place. A hyper-personalised experience can lead directly to KPIs like increased conversions, average order values, and revenue growth. (Gartner).
And while all these rising stats prove that consumer attitudes have gravitated towards online shopping for years, COVID-19 accelerated the shift. New habits have formed, and consumers are much more likely to seek out a personalised experience.
Designing Personalised Experiences in Ecommerce
The heart of personalisation is goal attainment. As such, the goals you set out for your personalisation efforts should be customer-driven.
It’s not about simply delivering what your business wants. You need to let visitors consume the experience how they prefer and help them achieve their goals at each stage in their journey.
Think of a business you interact with online — your favourite store, your bank, a vacation booking site — and recall the variety of goals you’ve looked to accomplish there.
Your needs from a home goods store may be quite different during the wedding season. You rely on your bank for a new set of information when buying a home, and your vacation preferences change depending on whether you’re travelling by yourself or with family.
Each visitor interacts with businesses in a multitude of ways, and truly powerful personalisation looks beyond who you are to what you are trying to achieve right now.
Site search, browsing data, product recommendations, landing pages, and all other interaction points should work cohesively to build a complete picture of each visitor across their journey.
Of course, this is easier said than done. While personalisation is an increasingly hot topic, most businesses are still in the early stages of understanding how to best utilise it.
The Role of AI in Ecommerce Hyper-personalisation
Advancements in technology, especially the increasing accessibility of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, have been a major driver of hyper-personalisation.
Adding intelligence to the user experience can provide real-time assistance to users that simply isn’t possible manually.
That’s because machines can crunch data quickly, enabling real-time optimisations and scalability. Companies can utilise the collected and processed data to recommend personalised products to every customer in real-time and thus design an individual, user-oriented shopping experience.
For instance, say a transportation service has an app offering public transportation directions. Algorithms could determine, based on travel speed, if a user is walking, biking, or driving, then recalculate the journey with the appropriate timing.
For organisations that rely heavily on content, intelligence can help direct content creation by identifying gaps in information that visitors are searching for. Perhaps a financial company sees a rise in visitors searching for information around automating investments — information like this can help content creators prioritise the rising topics their actual customers are interested in. Through natural language processing and machine learning, these trending topics can be identified quickly, without the hours of manpower that would be required to read through thousands of search terms and pull out trends.
Ecommerce Personalisation Technologies and Tactics
A major issue that digital businesses face when discussing personalisation is that there is no single tactic that defines it, and each class of technology comes with limitations.
It’s not as simple as, “We ran an A/B test, and now we are personalised.” There’s a whole spectrum of technologies involved, and creating your personalisation roadmap means making your own unique recipe of how much, or how little, you will rely on each one.
The table below contains some of the most common tactics used in both B2C and B2B ecommerce, and each one of these technologies is on the spectrum of personalisation. The way forward is to combine each of these technologies to build a comprehensive intelligence around user intent.
To get your visitors to their goal of the moment, you need to understand them and tailor your experience across every level these technologies offer.
Real-time personalisation requires noticing how visitors’ behaviour differs or aligns with their typical behaviour, identifying their current goal through their behaviour and the behaviour of similar users, as well as using insights across all levels of technologies to help them accomplish this goal.
[Personalisation Tactic #1]: Understanding Audience
Understanding each customer’s need is the very essence of personalisation. Satisfying that need takes a blend of the right technology and the knowledge of how to use it.
Whether it’s a new visitor or a familiar customer, you can assemble clues from how they entered your site to determine why they came to you. If you identify that intent immediately, you can shorten their customer journey and enhance their experience.
Did they come from an advertisement on social media? Did they look for a particular product or service on a search engine? Did they find you from a press article?
If you’re lucky enough to have a known visitor who perhaps purchased something or filled out a form, you can display items or content that is related to them.
🔑 Do this:
If you’re a sports retailer and have a customer who entered your site through a search engine with the term “bargain golf clubs,” your landing page could boost some clubs you have on sale along with other low-priced clubs at the top of the product grid.
If you’re an insurance company and customers are visiting via their mobile phone from a country out of your region, you could induce they are likely a client on vacation and show claim information on the homepage.
If you’re an electronics retailer and your visitor recently ordered a laptop, merchandisers may want to display some popular accessories for that computer, like a desktop porting station, an external memory drive, or a carrying case.
Thanks to digital experience platforms and machine learning, you can take care of this at scale and provide the most relevant content and products to your visitors.
[Personalisation Tactic #2]: Semantic Understanding for Personalised Search
The relative rarity of personalised search is a huge missed opportunity, as visitors using search convert at a 1.8 times higher rate than the average visitor.
And while the search bar is arguably the most important real estate on any site, search functions unfortunately may hurt as much as they help your customer experience. That’s because many search engines focus on keywords instead of the meaning of those words in context.
Search can be messy. Spelling mistakes, the use of broad terms, and differences in how people describe the same product can make accurate search results a struggle.
On a practical level, these challenges are the difference between dumb search and intelligent search. Most marketing platforms still search for words alone, which is a recipe for failure.
For instance, if a shopper searches for a “budget black laptop,” they probably want a black, low-cost computer. But a keyword search may instead deliver a page of low-cost black accessories for a laptop.
By comparison, an intelligent, semantic search considers the words in context, just as a human sales clerk would.
Intelligent search with semantic understanding capabilities is a huge advantage when it comes to happy customers. Brands, manufacturers, retailers, and distributors need to bring their business into the search engine to create guided, merchandising-driven selling experiences on their own.
Intelligent search solutions:
- Offer a set of selling capabilities beyond the search box
- Enable sellers to promote new products since a customer’s last visit
- Help in-store shoppers locate products on a kiosk
- Promotes add-ons for already-purchased products or products in the shopping cart
This means sellers can deliver personalized experiences and recommendations to customers searching and browsing across landing pages — eliminating the need to combine disparate products from multiple software vendors.
🔑 Do this:
If a user has shown interest in female products (e.g., skirts, dresses, bikinis, etc.) and then searches for generic terms like “shorts,” “shirt,” “exercise shirt,” or “running shoes,” you can use intelligent site search to give preference to female items in results, as the user is more likely to be female.
The experience of each user is hyper-personalised regarding the preferences that they have shown in the past. This is what semantic search has as its main goal: making it easy for your users to find what they’re looking for.
[Personalisation Tactic #3]: Targeting and Profiling
You can virtually accompany your visitors while they browse your site, just as a car salesman might walk with a customer around a showroom.
All along the way, a good salesman picks up clues on what kind of car suits his customers, what colour they like, what they can afford, and how soon they want the vehicle. Knowing the dealership’s inventory, he can then show them a car that matches their needs.
You can take a very similar approach online and can even use a trick that car dealers can’t: you can remain invisible while you do it.
A key to making this work is to let machine learning and AI process all that information and match it against your inventory in real-time.
Not only can machine learning help guide individuals at blazingly fast speeds, but it can also offer options a human might have missed by recognising patterns in the visitor’s past behaviour. Personalisation is NEVER matching them with a segment of buyers that had similar characteristics.
Technology has moved on and segmentation is fast becoming obsolete.
🔑 Do this:
If a clothing retailer knows that customers will soon be looking for festival wear, the retailer can create a landing page and add in the products they believe festival goers will be hunting for.
Machine learning then gets to work, boosting items that are performing well, have more stock available, and align to the visitor’s preferences.
Additionally, content marketers might create targeted, inspirational content around regional festivals and let AI provide the right content based on IP locations.
[Personalisation Tactic #4]: 1:1 Hyper-personalisation
Access to data is the first and most important step in great 1:1 – hyper-personalisation. Without the right software, to give you a complete picture of your customers on an individual level, crafting personalised email experiences is made simple..
But hyper-personalisation in ecommerce is a powerful tool, and when you do have access to a rich set of data about your customers, it can significantly change the products you show to individual shoppers. It requires rapid data aggregation and analysis, cross-channel deployment, and machine learning optimisation, but with those solutions in place, marketers and merchandisers can implement transformative personalized journeys at every touchpoint — including search, browsing, site layout, and content. It does all this for you in nano-seconds – autonomously.
🔑 Do this:
You’ve likely seen prompts and recommended products on retail websites before. “You Might Like…” and “Others Also Purchased…” are common prompts on ecommerce websites that signal a product recommendations engine at work. This is a fantastic personalised journey to provide your customers, and it comes to life by utilising a rich data set.
When search behaviour and browsing history drive your recommendations, and AI is in place to ensure that your search is always learning and getting better, you can deliver the most relevant and conversion-driving results to your customers.
For example, if you have a customer who looks at very high heels, then you might suggest shoes with stiletto heels and shoes with four- or five-inch heels.
If a customer browses several Louboutin slingback heels, then dynamic categories might suggest Shoes by Christian Louboutin or Evening Wear Shoes by Christian Louboutin, and display products matching those categories.





