Having spent time building a targeted email list, and your creative team has drafted some awesome emails. The problem then is email deliverability. So this guide is designed to overcome all the problems which inhibit that. If an email ends up in the junk folder, then did it ever even exist? For your customer, the answer is no. But don’t worry.
In this guide, we’re going to deep dive into email deliverability. And we’re going to show you how to keep your emails away from the dreaded spam folder. Ready to up your open rate and get more clicks to your website?
What is Email Deliverability?
Email Deliverability is the set of processes responsible for placing an email into your client’s inbox.
Inbox placement and delivery is a complex subject. Many factors are taken into account by mailbox providers before placing an email into your subscribers’ inbox.
How Email Reputation Impacts Email Deliverability
When you send an email campaign, mailbox providers run an initial set of vetting checks.
These are known as reputation checks.
And they are a bit like credit checks for email, affected by:
- Sender reputation
- Server / IP reputation used to dispatch the email
- Domain reputation of links in the content
- Email engagement metrics including bounce and spam complaint rates for your sender, domain, and server
Reputation checks are one of the most essential factors of inbox placement.
A bad reputation will see your inbox placement and open rates tank.
Let’s look at all the factors that are bound to email delivery reputation.
We’ll start with your sender’s reputation.
What is Sender Reputation?
Sender reputation is the reputation of the email address you are using to send out your email campaigns. Usually, your sender reputation is calculated on a scale of 0 to 100 to give you your sender score. But how exactly does sender reputation work? What factors increase or decrease your sender reputation?
Email Deliverability goes hand in hand with sender reputation. Here are five factors positively influencing sender reputation: consistent volume of email campaigns per week, few bounces, fewer complaints, no spam traps, and no blacklists.
1. Be Consistent with Your Volume
Try to distribute your email marketing campaigns evenly.
A consistent volume of email campaigns, without major drops or spikes, plays a significant role in sender reputation. For example, if you send out an email to your list twice a week, switching to three times a week will cause ripples. There will be times when you will want to send out more emails than usual. For example, over the busy Christmas period. But aim for a regular, consistent schedule where possible. Your list will soon get to know your schedule, which will help you increase open rates and click-throughs.
2. Keep Your Lists Clean to Crush Bounce Rate
Clean your lists, use Bouncer, NeverBounce, Data Validation, and Email List Verify, among others. Some other notable alternatives are ZeroBounce, MyEmailVerifier, Debounce, and Clearout. Bounces are emails that fail to reach the subscriber. Notwithstanding their impact on future email deliverability, they are a waste of resources. There are two types of bounce, soft and hard bounce.
What is Hard Bounce?
A hard bounce happens when you send a message to a mailbox that doesn’t exist. Perhaps someone used a fake email to sign up to your subscriber list, or have changed email providers. Either way, you don’t want those email addresses on your list.
What is Soft Bounce?
A soft bounce occurs when you send to a:
- Full mailbox
- recipient with an auto-reply / out-of-office message
You probably don’t want to remove these email addresses from your subscriber list. Usually, this will be a temporary issue. But if your messages are consistently bouncing, you might want to reconsider. Mailbox providers, such as Gmail, monitor the bounce messages. They then return undelivered emails to the email service provider.
A high bounce rate implies a poor list hygiene process. That could mean a list that is not contacted frequently or is purchased. Therefore, you need an email verifier to check the email addresses and be 100% sure that they are valid.
3. Spam Complaints = Death for Your List
When your subscribers hit the dreaded “Mark as spam” button, mailbox providers like Gmail and ESPs receive a notification. Mailbox providers automatically block even senders with a small number of complaints. It’s for this reason that we strongly discourage the use of purchased lists as they will see your spam complaints rocket.
4. Steer Clear οf Spam Traps
A spam trap is a fake email address that looks real, but it isn’t. Spam traps are set by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and blacklist providers to catch unscrupulous email marketers who have been harvesting emails.
They’re like honeypots that are published in a hidden location on the web. When spammers collect email addresses through harvester programs or purchased email lists, these fake email addresses often make it onto their lists. Sending even a tiny amount of emails to those email addresses automatically marks the sender as a spammer. They built their list unnaturally. Here’s a link to everything you need to know about Gmail Spam filters.
5. Whatever You Do – Don’t Get Blacklisted!
Blacklists are lists of sender domains (e.g. yourdomain.com) and servers or IP addresses that have been caught sending email spam. Send an email from a blacklisted server or domain, and the chances are it will land in junk (or not at all). There are over 100 blacklists for different purposes, and you need to stay off of every single one of them.
What Gets You Blacklisted
Falling foul of any of points 1-4 above. The good news is that if you get blacklisted once, there’s a strong chance you will be able to de-list your site/server. Repeat offenders, though, will have more trouble getting off the blacklist. To avoid that, SwiftERM continuously monitors blacklists to keep users safe. You can use the MX toolbox to check if your server or domain is blacklisted.
Why Authentication (DKIM, SPF, TLS) is Critical to Email Deliverability
As you’ve probably gathered by now, email deliverability is a complex topic. But it’s also an evolving one. Spammers are always looking for new loopholes and tricks. New ways to abuse your email inbox. On the flip side, mailbox providers like Gmail are catching up in keeping spam messages low, or out of sight altogether.
How Spammers Use Email Sender Spoofing
Sending an email on behalf of someone like [email protected] is easy. Change a few header values, and the ISP will think that Mark is trying to send out a message. With email spoofing, spammers can easily impersonate your brand’s email and send campaigns on your behalf. Right?
Well, fortunately, it’s not quite as simple as that. And mailbox providers are getting better at catching this type of spam. Most providers – certainly all major ones – will perform an ID check when receiving a new email.
Here’s How It Works
A mailbox provider receives an email from an address (say [email protected]).
- The provider checks the IP address where the message originated.
- Then, they check to see if that IP address has permission to send emails on behalf of yourdomain.com.
This is called authentication. But let’s clarify something:
Sending emails on behalf of another address is not necessarily a bad thing. Why? Because this is precisely what all email service providers (ESPs) do to deliver the campaigns you design and send. After all, you want to be sending emails from your branded domain.
Setting up authentication in your email marketing service of choice is highly recommended. It will hint to Hotmail, Gmail, and all other providers that you have given consent to send emails on your behalf. There are two main ways to set up email authentication: SPF and DKIM. SPF and DKIM are an item. They are complementary. What SPF lacks in ownership authentication, DKIM makes up for it in email validation.
6. Use SPF To Verify Your Sender IP
Setting up your SPF records is essential.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is an email validation system designed to prevent spam by verifying the sender’s IP address. An SPF record allows web administrators to designate which web hosts are authorized to send messages from a given domain.
When an SPF record is added to your website’s DNS, servers use it to verify that you are allowed to send emails from [email protected]. Simply put, SPF says you are the owner of the domain and are allowed to contact people using this domain name.
7. Use DKIM to Verify Ownership of an Email Message
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) indicates ownership of the email message by a particular organization. While the message is still in transit to the recipient, the organization’s signature is added to the email headers. Most email clients will check for a valid DKIM signature on incoming emails to identify who sent it.
This means DKIM is a working way to prevent email deliverability issues and increase your sender reputation with email services. The receiving mail server can identify the origin of the email marketing campaign.
Should You Use SPF or DKM?
Quick answer: You should use both. Unless you are an email marketing nerd, you probably don’t need to know precisely how SPF and DKIM work. But what you do need to know is that both authentication levers are required to reduce spam and improve email deliverability rates.
SPF and DKIM work together. For instance, DKIM alone does not guarantee that the sender’s server is permitted to send outgoing emails in the name of your website (your domain). Often, SPF on its own is powerless as many website owners research different web hosting services, and then choose shared hosting. With shared hosting, multiple sites share the same IP address. SwiftERM uses SendGrid for all sending on behalf of our clients.
8. Encrypt Your Email with TLS to Build Trust with Users and Mailbox Providers
By its nature, email is prone to information disclosure. Since most emails are transmitted in an unencrypted form, TLS is essential.
So what is TLS?
TLS is a form of encryption for email messages which protects the content from being read by entities other than the intended recipients. Email encryption may also be considered as a form of authentication. Gmail implements TLS for email delivery, but at the moment, it’s still an optional requirement.
And there is still no proof that unencrypted emails fail inbox placement on Gmail or other providers. Nevertheless, we believe that the TLS requirement will eventually become mandatory. For the time being, TLS-enabled emails will show a nice padlock icon on Gmail to notify your customers that your emails are encrypted.
Encrypt Your Email with a Third Party
Email encryption is a surefire way to ensure the deliverability and security of your emails. But sometimes, knowing how to do this and complying with all the which go along with it can be tricky to navigate.
While many email marketing software providers have an encryption feature in-built, if you’re sending emails via other methods, including Gmail and Outlook, a third-party provider, might be the solution to your problems. Doing this will not only help your email deliverability but several other email-related issues too.
You can prevent third-party access to your data, maintain control over sensitive data, and audit access to emails and attachments to name but a few!
How Infrastructure Impacts Email Deliverability
Email deliverability infrastructure is the software and hardware used to deliver your emails to your recipients. The infrastructure required to send emails at scale is not to be taken lightly. Setting up your infrastructure rather than using an ESP is very complex and cost-efficient.
There are several low-level protocols and standards that you must implement and adhere to. And you will quickly find that you need very specialized personnel to handle the operation. Frankly, it just isn’t worth the hassle. So what exactly affects email deliverability from an infrastructure standpoint?
The IP Address (Dedicated vs. Shared)
Two types of IP addresses related to email deliverability. Dedicated IPs, which are best practices for high volume senders, and shared IPs. So which do you need?
9. High Volume Sender? – Opt for a Dedicated IP Address
Dedicated IPs are exclusively used for your campaigns and senders. Email programs based on dedicated IPs flourish on consistent, healthy volume. Inconsistent volume, with dips and spikes, from a dedicated IP, will be counterproductive and classify you as a spammer.
10. Time-Sensitive Campaigns? – You Need a Dedicated IP Address
Dedicated IPs are used exclusively for your campaigns. There are no noisy neighbours or throttling because of issues caused by other senders.
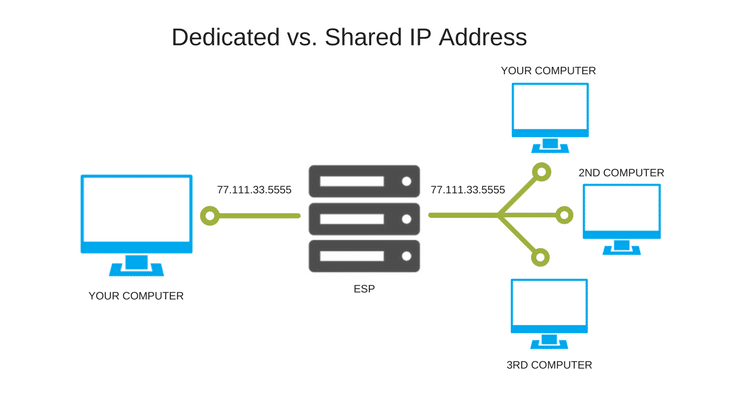
It’s a direct connection to the ISP and lightning-fast at delivering your messages over to your recipients. If there is any time sensitivity in your campaigns, we recommend that you opt for a dedicated IP.
11. Shared IPs for Everyone Else
If you send fewer than 200-300,000 emails per month, then you don’t need a dedicated IP. Your email marketing account would benefit more from using a shared pool of IP addresses. Shared IPs are only available in Email Service Providers. You can’t create a shared pool of IP addresses for your email marketing program.
Also, if you have concerns about your email list hygiene or the quality of your mailing list, you will be better served using a shared pool of IPs. They will help you get a lift on your email deliverability and combat delivery issues if you are below average on the IP pool.
12. Monitor Mailbox Provider Feedback Loops
Most major mailbox providers operate a feedback loop service to report back complaints to email service providers. When one of your subscribers hits the “Mark as spam” button, a request makes it back to the ESP through the feedback loop.
It’s imperative to unsubscribe and remove customers who complained from your mailing list immediately. The only way to do that is through monitoring various mailbox provider feedback loops. At the time of writing, there are more than 20 significant providers offering feedback loops. So implementation is not straightforward.
Some feedback loops, like the one offered by Gmail, are only available to exclusive members of M3AAWG (Messaging, Malware, and Mobile Anti-Abuse Working Group).
13. Set Up (and Monitor) an Abuse Reporting Mailbox
Some mailbox providers require email campaigns that land in their users’ inboxes to operate an abuse-reporting mailbox. It is an email address to forward abuse complaints to.
To ensure email deliverability, you must have an abuse-reporting mailbox setup and monitor it frequently. You can implement it through the use of an email header. Many mailbox providers without feedback loops will forward complaints to those mailboxes instead.
14. Set Up MX Records for Your Sender Domain
You need to have a valid MX record set up for your sender domain. Why? Because otherwise, some ISPs will automatically block your email. Time-Sensitive Campaigns? – You Need a Dedicated IP Address
Don’t neglect to check your email sender reputation for your domain name.
How Content Affects Email Deliverability
It might sound weird to you, but your email content is one of the factors affecting your deliverability. Poor content, bad designs, and unresponsive newsletter templates can break your deliverability. So, what can you do to avoid delivery issues and boost your reputation?
15. Send Relevant Content That Your Subscribers Want to Read
Will your subscribers benefit from your email campaign? Think before you send it! It doesn’t get simpler than that. Ask yourself – do my subscribers expect this type of content? Do your subscribers expect offers about laptops, but you send them the latest movie blockbuster?
Chances are that they will end up unsubscribing. Or, even worse, reporting you.
Hyper-personalisation and preference centres help with this. But it all comes down to sending familiar content to your subscribers.
16. Looks Matter: Be Consistent with Your Design
Let’s see an example from the shoe giant, Nike: We don’t need to tell you how important branding is to marketing. Your website and other marketing materials will have a consistent look. Your email campaigns should be the same.
It’s vital to maintain brand consistency throughout your newsletters. Your subscribers are familiar with your brand identity. They won’t expect massive design changes between campaigns. Of course, while your newsletter images will attract attention, don’t forget to invest in an equally attractive email copy to keep your email subscribers engaged.
17. Mobile-Friendly Designs Are No Longer Optional
Did you know that almost 50% of email opens now occur on mobile devices? This means there’s no excuse for sending campaigns that look great on a desktop or web client but suck on mobile.
There is a correlation between the complaint rate (or spam-iness) of your campaign and the absence of mobile compatibility. A campaign that looks out of place on mobile devices will disengage subscribers. And in some cases, it can lead them to unsubscribe since they cannot use their preferred mobile email client to read your brand’s newsletters.
So make sure your campaigns are mobile-friendly, and have the right newsletter images, and copy to avoid falling into one of the most common pitfalls of email deliverability.
18. Be Careful with URL Shorteners
URL shorteners are those handy little tools that take a long URL and convert it into a short version. For example, they may take:
https://swifterm.com/courses/set-your-email-in-motion-for-all-businesses/
And convert it to:
They are useful for cutting down the length of your URLs, but they are also good at masking where a link goes. For instance, the shortened link above does not indicate its final destination. This is why spammers commonly use link shorteners.
They want to hide their malicious websites and blocked domains from users and mailbox providers. Major link shorteners are public services and, therefore, nothing stops spammers from using them to mask their URLs.
We strongly advise against using these services as part of your email marketing routine. Link shorteners have benefits, but they are outweighed by the shortcomings related to email deliverability. If you must use link shortening as part of your email campaigns, we recommend implementing your own.
Alternatively, you can set up a tool like YOURLS, Phurl, and Rebrandly’s URL Shortener.
URL shorteners are a great way to improve the look of your email marketing campaigns. At the same time, URL shorteners entail the risk of unknowingly visiting an unreliable website.
19. Don’t Use Spammy Subject Lines or Content
Your subject line is the only thing your subscribers read before opening your email campaign. It has also been proven that mailbox providers, such as Gmail, “read” your subject lines and content and decide whether it contains spammy keywords or not.
No one knows the exact implementation of Gmail or Outlook’s algorithm for classifying messages as spam. But a good start would be to avoid any spammy terms such as those listed here. CAPITALS and misleading prefixes (such as RE: or FW:) also trigger spam filters.
Why start your subject with ’RE:’, anyway, when you can get so much more creative?
20. Don’t Use Free, Personal Email Addresses for Your Campaigns
Your campaigns must fully represent your brand. So there’s no point sending emails from your personal Gmail address. The reason is simple: A Gmail address is a personal email address. This means your email campaign will most likely be considered spam by the various filters used by email service providers.
Ergo: it will not be delivered. So use a professional email address from a domain name recognised by your recipients. From a technical standpoint, Gmail and other ISPs implement an extra layer of authentication called DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance).
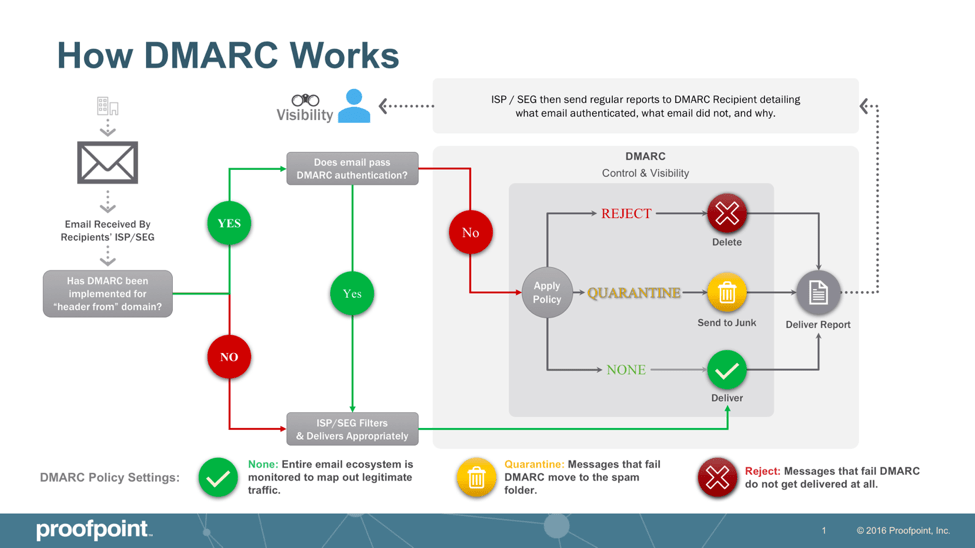
The popular email provider changed its policy a few years back and decided to penalise emails sent from Gmail addresses outside of Gmail. The reason email providers adopt it is that it provides an additional safety measure. There are still instances where SPF and DKIM checks are not enough to ensure the recipient’s safety. DMARC adds an extra level of cryptography.
21. Always Include a Plain-Text Version Along with Your HTML Campaign Version
Plain-text campaigns! Sent no-one ever… An email campaign without visuals is usually dull, right? But what if I told you that it is, in fact, one of the best ways to increase your email deliverability?
Email clients are smart. They will display the most compatible version of your email campaign based on your subscribers’ settings. While not fancy, this is a good practice for email deliverability purposes.

Plain text works because all recipients will be able to see your message.
That’s a win for your deliverability!
22. Pay Attention to Image/Text Ratio (But Don’t Sweat It Too Much)
Nowadays, the image-to-text ratio plays a less critical role in the spam filters of major inbox providers. But to maximise email deliverability, it’s still something you should be aware of.
Spam Assassin recommends a minimum of 60% text and a maximum of 40% images in your email campaigns. Our tests and those in the industry concluded that there is less of an issue with image/text ratio when other factors are satisfactory.
23. Use Double (Rather Than Single) Opt-In for Your Lists
Opt-in is the explicit permission of a customer, or intended recipient of an email, to allow a marketing team to send messages with promotional information about their brand.
There are two common forms; single opt-in and double opt-in.
What is Single Opt-in?
An email address is added by any means to a mailing list. However, no process is followed to ensure that the address belongs to whoever submitted it, or that the owner gave any form of formal permission. In other words, the email owner has not confirmed their consent to be added to the list.
What is Double Opt-in?
An email address is added by any means to a mailing list. A confirmation email is sent to verify that the person the email belongs to consents to receiving messages.
This is generally done by clicking a confirmation link. On occasion, consent can also be given externally, even offline. So, double opt-in registration is when confirmed consent of an email’s owner to receive messages is requested.
Double opt-in helps protect your mailing list from spambots and other invalid signups. You can expect the size of your mailing list to be slightly smaller than a single opt-in mailing list. But on the plus side, double opt-in is guaranteed to result in better email deliverability and inbox placement.
Engagement rates skyrocket for double opt-in mailing lists. This helps your sender reputation and your email deliverability as a whole. This higher probability of subscriber engagement makes inbox providers (such as Gmail) place your email in your subscribers’ inbox.
24. Only hyper-personalisation gives each subscriber exactly what they want
A significant factor in email deliverability is sending relevant content that your subscribers want to read. Unfortunately, this is not always possible for big brands with large mailing lists.
The solution is to use segmentation to create subsets of your mailing list with common interests. Hyper-personalisation software is unique and personal to the recipient and does all of the above for you.
It identifies product selections most relevant to each consumer and calculates when they are most likely to be interested, using send-time optimisation to deliver it at exactly the right time.
To learn more about the distinctions between the top 30 hyper-personalisation vendors, check out this article.
25. Make It Easy to Unsubscribe
This might sound a little counter-intuitive. But you want to make it super easy for your list members to unsubscribe. Hiding your unsubscribe links using various font sizes and colour techniques only makes your subscribers lose patience and trust.
Worse still, they could mark your email as spam instead of unsubscribing. The industry standard for complaints is 0.1%. This means that sending a campaign to 10,000 subscribers gives you only ten tickets to the “Mark as spam” button.
Any more than that and your campaign is over the threshold. Which will put your sender reputation in jeopardy. A footer offering a no-tricks unsubscribe link is a great way to keep your complaint rate low and maintain a high inbox placement. We cannot overstate the importance of making your unsubscribe links obvious.
26. Don’t Use a “No-Reply” Sender Address
“Do not reply” email addresses look like “[email protected]” and serve as a black hole for incoming mail. Marketers often send their campaigns from such do-not-reply email senders. It happens. But, more importantly, it happens A LOT.
These email addresses give the wrong idea to your users. Why should they not reply? Don’t you want to hear from them? There is more than one reason to avoid no-reply addresses. But above all, it makes you look unprofessional and unapproachable. It also massively affects your email deliverability and open rates.
Follow the steps in this guide to maximise the deliverability of your emails. Your engagement stats will skyrocket. If you have any questions or comments, we would be pleased to receive them below.






One Response
Thanks, this is very informative and helpful.