In today’s digital era, email remains one of the most powerful channels in a marketer’s toolkit. With saturated inboxes and increasing consumer expectations, simply sending broadcast emails is no longer sufficient. Organisations are investing heavily in technologies that promise higher engagement, better conversion rates, and smarter automation.
Two dominant strategies have emerged in the enterprise landscape:
- Autonomous Machine-Learning Hyper-Personalised Email
- Segmented and Triggered Email Solutions
Both aim to enhance relevance and performance, but they differ profoundly in their approach, scalability, cost structure, and returns. This blog post explores these differences in depth, with particular emphasis on the cost of staff and resources required to operate traditional segmented/triggered systems, compared to the efficiency and ROI potential of autonomous ML-driven personalisation.
In the realm of marketing, autonomous hyper-personalisation signifies a new era where technology tailors experiences to each user.
Table of Contents
This blog post examines the impact of autonomous hyper-personalisation on email marketing strategies.
- Introduction
- The Evolution of Email Marketing
- What Are Segmented and Triggered Email Solutions?
- What Is Autonomous ML Hyper-Personalised Email?
- Technical Architecture: Manual vs Autonomous
- Staffing and Operational Costs: A Critical Comparison
- Performance and Returns: Metrics That Matter
- Scalability and Speed to Market
- Challenges and Risks
- Case Studies and Industry Trends
- Decision Framework: Which Strategy Fits Your Business?
- Conclusion
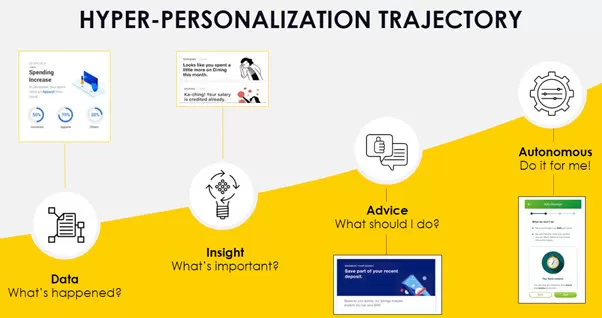
1. Introduction
Email marketing has come a long way from mass sends of generic content. The pressure to deliver meaningful user experiences has driven innovation in segmentation, automation, and predictive personalisation. Organisations are increasingly questioning whether traditional segmented approaches are delivering the expected ROI, especially when weighed against staffing costs and operational complexity.
At the centre of this debate is the rise of autonomous hyper-personalisation systems that promise real-time personalisation at scale — adapting content, send time, frequency, and offers without the need for manual rules or audience definitions.
Understanding the differences between legacy methods and intelligent automation is crucial for modern enterprises seeking sustainable growth, competitive advantage, and optimal utilization of human capital.
2. The Evolution of Email Marketing
In the early 2000s, email was a novelty — consumers were eager to receive newsletters. Marketers relied on simple lists and basic personalisation (e.g., name tokens). As adoption grew, so did sophistication:
- Static Segmentation based on attributes like demographics and purchase behavior.
- Triggered Emails that respond to user actions (e.g., abandoned cart).
- Dynamic Content Rules that insert banners or offers based on predefined criteria.
- Sophisticated Automation Engines that map journeys with hundreds of rules.
Today, the frontier of personalisation uses machine learning (ML) and AI systems to infer customer preferences and optimise interactions autonomously — often without human intervention once configured.
3. What Are Segmented and Triggered Email Solutions?
Segmented and triggered emails have been mainstream for over a decade. They are foundational in most CRM and marketing automation platforms.
3.1 Segmentation
Segmentation divides audiences into distinct groups based on criteria such as:
Exploring the potential of autonomous hyper-personalisation systems can dramatically improve engagement metrics.
- Demographics (age, location, gender)
- Behavior (purchase history, open rates)
- Engagement status (active, lapsed, VIP)
- Lifecycle stage (new customer, repeat customer)
These segments are then targeted with tailored messaging.
3.2 Triggered Emails
Triggered emails are based on user behavior or specific events:
- Welcome series after subscription
- Cart abandonment reminders
- Re-engagement campaigns after inactivity
- Post-purchase follow-ups
Unlike broad segmentation, triggered emails respond to known actions, aiming to reach users with relevant content at predetermined moments.
Strengths
- Familiar and easy to implement
- Predictable workflows
- Good for basic lifecycle messaging
Limitations
- Static — require manual definitions and updates
- Rules grow complex with scale
- Dependent on ongoing staff effort to maintain and optimize
- Limited personalisation beyond defined segments
4. What Is Autonomous ML Hyper-Personalised Email?
Autonomous ML hyper-personalisation refers to systems that leverage machine learning algorithms to tailor email content, timing, frequency, and offers at the individual level, automatically. Instead of manually defining segments, the system learns patterns and predicts optimal actions for each recipient.
Key capabilities include:
- Predictive modeling for individual user preferences
- Dynamic content assembly based on user behavior
- Optimized send timing per user
- Automated offer/e-mail type selection
- Continuous learning and adaptation
These systems use data across multiple dimensions — behavioural, transactional, contextual — and infer insights that drive deeply personalised campaigns that evolve without constant human intervention.
What Makes It “Autonomous”?
While traditional personalisation may still need rules and segment definitions, autonomous systems operate with:
- Minimal manual rules
- Continuous feedback loops
- Automated decision-making
- Real-time content adaptation
- Self-optimization of KPIs
This enables campaigns that feel personal and timely for each individual recipient.
5. Technical Architecture: Manual vs Autonomous
5.1 Segmented/Triggered Email Architecture
- Data ingestion → CRM → Manual rule definition
- Segment creation and upkeep
- Rules based on business logic
- Triggered workflows tied to events
- Human monitoring and adjustment
This architecture demands specialized staff — analysts, campaign managers, copywriters, and optimization experts — to keep segmentation relevant and workflows efficient.
5.2 Autonomous ML Architecture
- Unified data platform
- Real-time event collection
- Machine learning models trained on historical and live data
- Automated decision engines
- Continuous self-improvement
Here, ML models infer relevance and optimize without manual segment definition. Human intervention is mostly at strategy level, not execution level.
6. Staffing and Operational Costs: A Critical Comparison
One of the most significant strategic considerations for enterprises is staffing cost — not just licensing fees for tools.
6.1 Segmented & Triggered Email: Human Dependency
Driving traditional segmented campaigns requires a multidisciplinary team:
Roles Typically Required:
| Role | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Data Analysts | Extract, validate, and segment data |
| Campaign Managers | Design workflows, set rules, schedule sends |
| Content Strategists | Tailor messaging for segments |
| Designers | Craft visuals and templates |
| QA & Testing | Ensure correct rendering and user experience |
| Optimization Specialists | Track and refine performance |
Each of these roles has costs — salaries, training, turnover, and time to onboard new personnel.
Estimated Operational Costs
- Larger organisations may budget 6–12 FTEs (full-time equivalents) dedicated to email campaign strategy and execution.
- Mid-size companies may allocate 3–6 FTEs.
- Smaller businesses can find even maintaining 1–2 specialists challenging.
Beyond salaries, there are hidden costs:
- Time spent on manual workflows
- Opportunity cost of staff focusing on repetitive tasks
- Expenses for segmented audience reports and manual QA
This operational overhead scales with the number of campaigns and complexity of customer journeys.
Concise overview of website’s key features and offerings.
By leveraging autonomous hyper-personalisation, marketers can dynamically adapt their strategies.
Autonomous ML systems shift much of the workload from manual execution to algorithmic optimization.
Roles Needed in an Autonomous Approach:
- Data Engineer / ML Specialist — to configure and maintain infrastructure
- Strategic Marketing Lead — to define goals and business constraints
- Creative Producer — for high-level content strategy
This team is typically smaller because:
- The system automates segmentation and optimization
- Real-time decisioning replaces manual rules
- Learning frameworks reduce repetitive tasks
Estimated Operational Costs
- Larger enterprises might allocate 2–4 specialists
- Mid-size companies might need 1–2 specialists
- Small companies may leverage a marketer plus a shared data resource
Even after factoring in higher platform licensing costs, the reduction in human capital often produces a net cost savings.
6.3 Quantifying Cost Differences
| Cost Component | Segmented / Triggered Email | Autonomous ML Email |
|---|---|---|
| Staff Headcount | High (3–12+ FTEs) | Low (1–4 FTEs) |
| Manual Rule Maintenance | Heavy | Minimal |
| Skill Level Required | Mid to High | High (for setup, then lower) |
| Platform Complexity | Moderate | High initially |
| Ongoing Operational Cost | Substantial | Significantly Lower |
From an operational perspective, autonomous ML systems can dramatically lower staffing costs while automating complexity that would otherwise require ongoing human intervention.
7. Performance and Returns: Metrics That Matter
Beyond staffing costs, performance outcomes are paramount. Return on investment (ROI) depends on engagement, conversion, retention, and revenue per email.
7.1 Traditional Segmentation: Expected Returns
Segmented and triggered campaigns typically yield:
- Higher open rates than broadcast email
- Moderate conversion gains with lifecycle targeting
- Incremental lift from behavioral triggers
However, as segmentation rules proliferate, diminishing returns can set in:
- Segments become too narrow
- Audience fragmentation reduces statistical power
- Manual optimization plateaus
7.2 Autonomous Hyper-Personalisation: Expected Returns
Autonomous systems drive returns across multiple dimensions:
1. Relevance
Each user receives optimized content, not just segment-level messaging.
2. Timing Optimization
ML models predict when each recipient is most likely to engage.
3. Offer Personalisation
Recommended offers based on individual preferences and buying patterns.
4. Continuous Learning
Models adapt over time, improving results without manual intervention.
7.3 Comparative Performance
| Metric | Segmented | Autonomous ML |
|---|---|---|
| Open Rate | Good | Excellent |
| Click-Through Rate | Better | Significantly Higher |
| Conversion Rate | Moderate | High |
| Revenue per Email | Moderate | Strong |
| Engagement Lift Over Time | Limited | Continuous |
Studies and industry benchmarks increasingly show that ML-driven personalisation outperforms static segmentation, particularly as data richness and complexity increase.
8. Scalability and Speed to Market
8.1 Scalability with Segmented Emails
Each new product, persona, or campaign dimension requires:
- New segment definitions
- Manual content adaptation
- Workflow updates
- Testing and QA
This doesn’t scale well in fast-moving markets.
8.2 Scalability with Autonomous ML
Once the data infrastructure is in place:
- Personalisation scales with minimal incremental work
- New segments are inferred, not defined
- New campaigns benefit from existing models
- Global audiences are addressed with personalised experiences
Autonomous systems handle scale organically. The more data they ingest, the better they optimize.
9. Challenges and Risks
9.1 Segmented / Triggered Solutions
Challenges:
- Rule complexity becomes unmanageable
- Staff burnout from repetitive task load
- Siloed data leads to suboptimal segments
- Limited adaptability to changing behavior
9.2 Autonomous ML Systems
Challenges:
- Higher initial investment in technology and data infrastructure
- Need experienced data scientists for setup
- Risk of over-reliance on automation without strategy alignment
- Transparency concerns (black-box models)
However, these challenges are increasingly manageable with mature platforms and clear governance practices.
10. Case Studies and Industry Trends
Macro Trends
- Enterprises consolidating tools into centralised ML platforms
- Increased use of predictive analytics in customer engagement
Hypothetical Comparisons
Brand A: Segmented Approach
- 8 FTEs managing campaigns
- 15–20 segments, dozens of rules
- Incremental improvement year over year
Brand B: Autonomous ML
- 3 specialists managing strategy
- Models optimizing every send
- Engagement increases quarter over quarter
- Staffing costs reduced by 50%+
Real-world data from vendors indicates substantial uplifts in click-through and revenue per email when moving to ML personalisation versus segmented sends.
11. Decision Framework: Which Strategy Fits Your Business?
Use this framework to evaluate your situation:
Business Size and Resources
- Limited staff → Autonomous ML offers efficiency
- Large team and simple products → Segmentation may suffice short-term
Data Complexity
- High data volume and varied customer behavior → ML benefits
- Low complexity → Manual may work initially
Strategic Priorities
- Focus on scaling personalisation → ML
- Compliance or strict rule governance → Manual might fit
Cost vs Return
- Consider total cost of ownership (TCO), including staffing
- Autonomous ML often delivers better ROI over 24–36 months
12. Conclusion
The distinction between autonomous machine-learning hyper-personalised email and segmented or triggered email solutions is not merely technical — it is strategic.
Segmented and triggered approaches have served marketers well, providing essential lifecycle communication and basic personalisation. However, they rely heavily on human expertise and ongoing manual effort, resulting in higher operational costs and limited scalability.
By contrast, autonomous ML-driven systems offer:
- Real-time personalisation at the individual level
- Continuous performance optimization
- Lower staffing requirements
- Higher returns in engagement, conversion, and revenue
For enterprises seeking to future-proof their email strategy, investing in autonomous machine learning represents not just a technological upgrade but a structural shift toward efficiency, scale, and competitive advantage.
The cost of staff needed to maintain traditional segmented solutions — from analysts to campaign managers — can be significantly higher than the leaner teams required to support autonomous systems. When combined with superior performance and operational efficiency, ML-driven hyper-personalisation is rapidly becoming the benchmark for best-in-class email marketing.
- Executive comparison table
- Staffing cost breakdown table
- ROI impact model
- Architectural flow diagrams
- Total cost of ownership (TCO) comparison model
- Infographic concepts your design team can build
The benefits of autonomous hyper-personalisation extend beyond simple metrics; they redefine how brands interact with users.
1️⃣ Executive Comparison Table (Board-Level View)
With autonomous hyper-personalisation, each email can be tailored to the specific interests of the recipient.
Autonomous ML vs Segmented & Triggered Email
| Dimension | Segmented / Triggered Email | Autonomous ML Hyper-Personalised Email |
|---|---|---|
| Personalisation Level | Segment-based | Individual-level |
| Optimisation Method | Manual rule adjustments | Continuous algorithmic learning |
| Campaign Setup Time | High | Low after implementation |
| Staffing Requirement | 3–12+ FTEs | 1–4 FTEs |
| Scalability | Limited by human capacity | Scales automatically with data |
| Speed of Iteration | Slow (weekly/monthly cycles) | Real-time |
| Performance Plateau Risk | High | Low (continuous improvement) |
| Revenue Per Email | Moderate | Significantly higher |
| Operational Complexity | Grows exponentially | Managed by system |
| Long-Term ROI | Incremental | Compounding |
Executive takeaway:
Traditional systems scale headcount. Autonomous systems scale intelligence.
Integrating autonomous hyper-personalisation into marketing strategies can greatly improve overall customer satisfaction.
2️⃣ Staffing Cost Breakdown (Detailed Operational View)
This table is particularly powerful for CFO and COO audiences.
Typical Annual Staffing Costs (Mid-to-Large Enterprise Example)
| Role | Segmented Approach (FTEs) | Avg Annual Cost per FTE | Total Cost | Autonomous ML (FTEs) | Total Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Campaign Managers | 3 | $85,000 | $255,000 | 1 | $85,000 |
| Data Analysts | 2 | $95,000 | $190,000 | 1 | $95,000 |
| CRM Specialist | 1 | $90,000 | $90,000 | – | – |
| QA / Testing | 1 | $75,000 | $75,000 | – | – |
| Optimisation Specialist | 1 | $100,000 | $100,000 | – | – |
| ML/Data Engineer | – | – | – | 1 | $130,000 |
| Strategic Lead | 1 | $120,000 | $120,000 | 1 | $120,000 |
To maximize ROI, businesses must consider the impact of autonomous hyper-personalisation on customer relationships.
Estimated Total Annual Staffing Cost
As businesses shift towards autonomous hyper-personalisation, they unlock new avenues for customer engagement.
- Segmented Model: ~$830,000
- Autonomous ML Model: ~$430,000
Annual staffing delta: ~$400,000+ savings
By applying autonomous hyper-personalisation techniques, brands can enhance the relevance of their offerings.
Embracing autonomous hyper-personalisation can lead to significant advancements in deliverability rates.
Over 3 years, that’s $1.2M+ in human capital cost difference, before factoring performance uplift.
3️⃣ ROI Impact Model
Revenue Impact Illustration
Let’s assume:
- 5 million emails per month
- $0.40 revenue per email (segmented model baseline)
Segmented Model Annual Revenue
5M × 12 × $0.40 = $24M
Now assume autonomous ML increases revenue per email by 20% (a conservative uplift in advanced deployments).
New RPE: $0.48
5M × 12 × $0.48 = $28.8M
Annual Revenue Lift: $4.8M
Combined with staffing reduction:
- +$4.8M incremental revenue
- +$400K staffing savings
- = ~$5.2M annual impact
This is why autonomous systems fundamentally shift ROI conversations.
4️⃣ Architecture Diagrams
These can be converted into professional visuals.
A. Segmented / Triggered Email Workflow
Data Sources
↓
CRM Database
↓
Manual Segmentation
↓
Rule Creation
↓
Campaign Workflow Setup
↓
QA & Testing
↓
Scheduled Deployment
↓
Performance Review
↓
Manual Optimisation
Characteristics:
• Linear
• Human-dependent
• Iterative but slow
• Resource-heavy
B. Autonomous ML Workflow
Unified Data Layer
↓
Real-Time Event Stream
↓
Machine Learning Models
↓
Individual Decision Engine
↓
Dynamic Content Assembly
↓
Optimised Send Time
↓
Automated Deployment
↓
Continuous Learning Loop
Characteristics:
• Circular (self-improving loop)
• Adaptive
• Real-time
• Human-light
5️⃣ Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Comparison Model
3-Year View
| Cost Component | Segmented Model | Autonomous ML |
|---|---|---|
| Staffing (3 years) | $2.49M | $1.29M |
| Platform Licensing | $450K | $900K |
| Training & Onboarding | $180K | $120K |
| Operational Inefficiency | High | Low |
| Revenue Uplift | Moderate | High |
Net Strategic Position
Even if autonomous platforms cost more in licensing, the human capital reduction + revenue lift typically outweigh platform premium within 12–18 months.
The landscape of email marketing will be transformed through the power of autonomous hyper-personalisation.
Understanding the implications of autonomous hyper-personalisation will be crucial for future marketing efforts.





