Selling over the Internet was, and still can be, a big step for many businesses. But just as ecommerce is now a daily choice for many consumers, the growth of mobile commerce suggests that it too will become as popular.
Businesses of all sizes looking to utilise a new way of allowing customers to purchase products will benefit from mobile commerce, which offers a range of advantages to both the business and the purchaser.
So what is mobile commerce?
Mobile commerce, also known as m-commerce or mCommerce, refers to the sale of goods through mobile devices – such as mobile phones or tablet computers – over a wireless internet connection. Mobile commerce requires different considerations than ecommerce because of a range of factors, both situational (people can use a mobile device anywhere) and technology-based (smaller screens).
As mobile devices become more commonplace, and consumers spend more time using them over and above traditional computers with internet connections, mobile commerce is likely to emerge as a dominant method of marketing and selling among businesses of all sizes.
What are the advantages of mobile commerce?
Mobile commerce offers a range of advantages to businesses both large and small. The number of people owning and regularly using mobile devices continues to grow, providing a large – and growing – marketplace for a variety of goods and services.
- Wide reach: mobile commerce allows consumers to buy, and be marketed to, wherever they can get an internet connection. This offers considerable advantages over ecommerce, which must rely on a traditional internet connection such as over Ethernet. This also means that you can run your business from any location, reducing the need for an office space. Improvements to infrastructure are increasing the speed and reliability of mobile internet access, making mobile commerce a sure-fire growth industry in the short and medium term future.
- The personal touch: selling over mobile devices can yield a very personal encounter for the consumer, especially if the services and products you offer are individually tailored. Mobile devices are often kept very close and so by providing the right kind of service retailers can capture the attention of consumers more easily.
- Reduced need for skilled consumers: mobile commerce reduces the need for the consumer to have certain skills (e.g. being able to use search engines or online checkout processes)
- Bespoke applications: you can build custom applications to spread your brand and also streamline the purchase process.
- Hyper-personalised product selection software, using predictive analytics technologies, the distinctions between which are critical, identify consumer’s future behaviour, then rank every SKU by greatest likelihood of “that individual consumer” will purchase from all the SKUs you have listed, in order of greatest likely buying propensity. In other words, the ones they love best. CLV soars and RoR is all but eliminated.
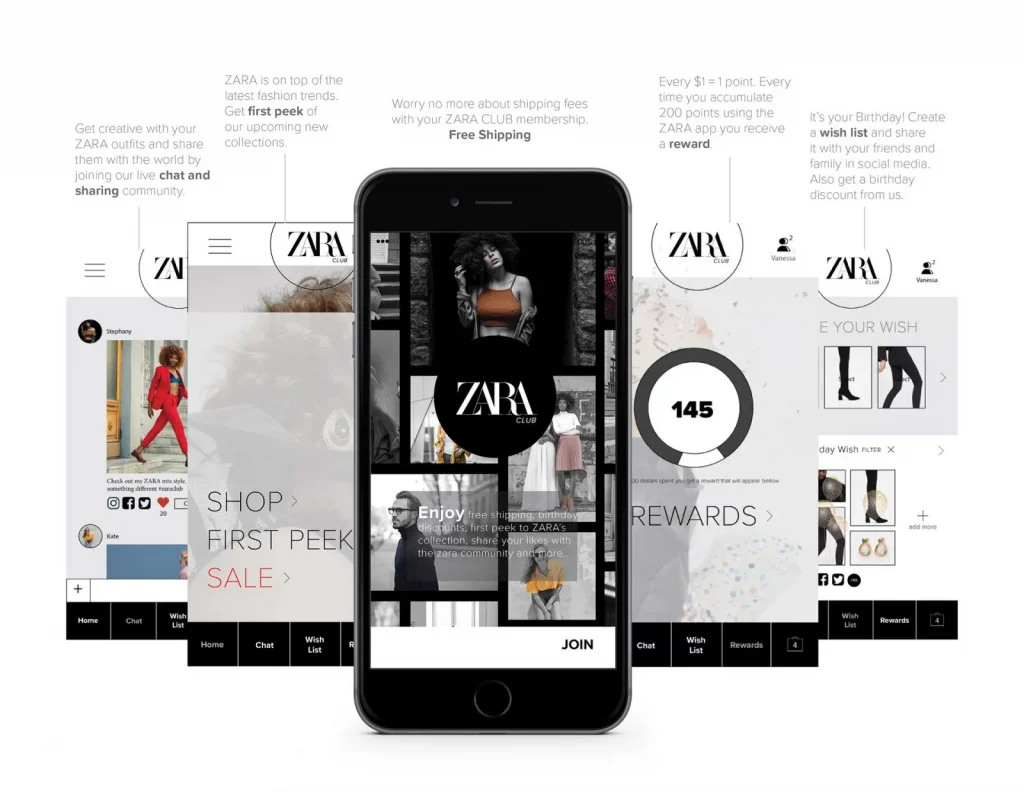
What are the disadvantages of mobile commerce?
Mobile commerce is a growing sector and analysts expect significant growth in the next few years. At the current time, there are some disadvantages from a retailer’s point of view. As with any new investment, consideration must be given as to whether the disadvantages outweigh the potential gains.
- Smaller screens: the smaller and less vivid screens of mobile devices give less of an opportunity for retailers to sell products with eye-catching images and graphic design. The amount of marketing collateral that can be delivered is reduced.
- Investment in a growing market: business investment in mobile commerce can be risky due to the rapid-fire pace of the market and its ability to shift quickly.
- Speed of delivery: mobile devices are less powerful than personal computers which means mobile websites must be optimised for the technology. This means a potentially reduced appeal, in addition to the man-hour costs of removing inappropriate content such as flash videos and plug-ins.
- Security: Although mobile security is improving regularly, there is still reluctance among some consumers to conduct transactions over a mobile device. Likewise, wireless networks – particularly those with widespread access such as mobile phone networks – will generally provide greater opportunities for hackers than the standard ‘internet’.
- Difficult user interface: there is often a learning curve when it comes to handheld devices. Mobile websites and commerce gateways must be built with usability in mind, to reduce the number of customers who abandon the purchase due to frustration, and this can add significantly to the cost.
Mobile commerce and your business
Although mobile commerce refers to selling your products via mobile devices, there are several different methods of offering mobile purchasing to your customers. The two most common are mobile websites and applications.
Mobile Websites
Mobile websites are generally cheaper than applications, especially if you use your existing site as a template rather than design a new mobile version from scratch.
Mobile websites also offer greater reach than applications, which are limited to consumers on platforms that support applications. Some consumers even avoid applications altogether, whereas all those who want to browse the internet on handheld devices must use internet browsers, and therefore can access mobile sites.
Furthermore, you’ll need to design just one mobile site, whereas if you go the app route you’ll need a variety of apps to suit the number of platforms available, such as iPhone and Android. The number of platforms is likely to continue growing.
The other advantage of a website is that you won’t need third-party approval to gain customers. Applications going into the most popular online application stores often have to conform to stringent guidelines before they are accepted. Mobile sites can be customised, with no constraints on the design or functionality.
APPLICATIONS
Applications – custom programs designed specifically for your company – run on smartphones, and the smartphone market is growing significantly. Applications are generally more expensive than mobile websites, but they do offer some advantages.
Users of smartphones have more money, generally, and so applications can yield a better return for the business, although this will depend on the type of product on offer. In terms of functionality, apps also come out ahead, with their ability to leverage the functions of the device itself including GPS (for location-based products and services) and the in-built camera to provide a more rewarding experience.
Additionally, applications provide greater visibility than mobile websites. Online stores for apps are easy to browse, with apps split into genre categories as well as popularity. This compares favourably to a website, which customers must either type in directly to their browser or search on Google. This can be something of a minefield, particularly for competitive products.
We should make a special mention of augmented reality. If ever there is a reason to shop with a mobile phone, and there is now a generation for whom a tablet or PC is entrenched in the psyche, it is AR. Apps allow you to see yourself in clothes, wearing make-up, and adorning your life with products, all by apps specifically written for mobile commerce.





